Introduction
Electric cars (EVs) are becoming increasingly popular as people seek cleaner, greener means of getting about. However, how long does it take to charge an electric vehicle is a common topic of inquiry. The size of the vehicle’s battery and the type of charger being used are just two variables that affect the answer to this question. This post will examine the various EV chargers available and how long does it take to charge an electric vehicle with each fully.

Facts About EV Charging Time
EV charging time varies based on the charging level and battery size. Level 1 chargers can take up to 20 hours, Level 2 chargers can fully charge an EV in 4-8 hours, and Level 3 chargers can charge up to 80% in 30 minutes. Larger batteries take longer to charge than smaller ones. Understanding these facts about EV charging time is essential for planning journeys and ensuring you have enough time to recharge your EV.
How Long Does it Take to Charge an Electric Vehicle?
How long does it take to charge an electric vehicle is a frequent topic of inquiry. The answer to this question is conditional on several variables, such as the capacity of the battery, the charging method, and the rate at which the battery is charged. Depending on these circumstances, the time required to charge an electric vehicle fully might range from 30 minutes to several hours.

Level 2 chargers, the most prevalent form, can fully charge an electric vehicle in 4-8 hours. Fast chargers, often called Level 3 chargers, can replenish a battery in a fully charged electric vehicle in as little as 30 minutes. The size of the battery also affects the charging time; bigger batteries take longer to charge. It is crucial to build adequate time for charging stops when planning a long trip in an electric vehicle.
Types of EV Chargers
-
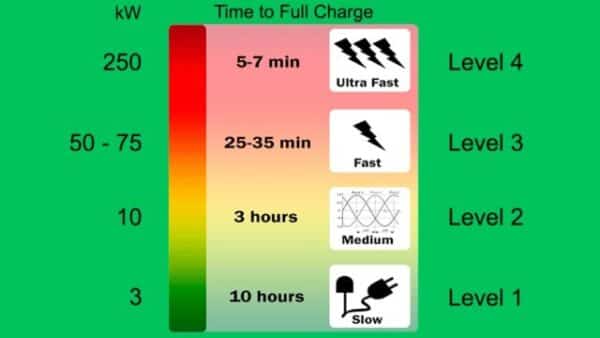
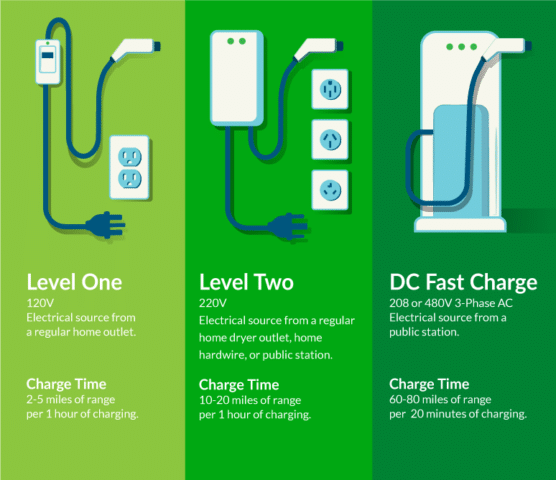
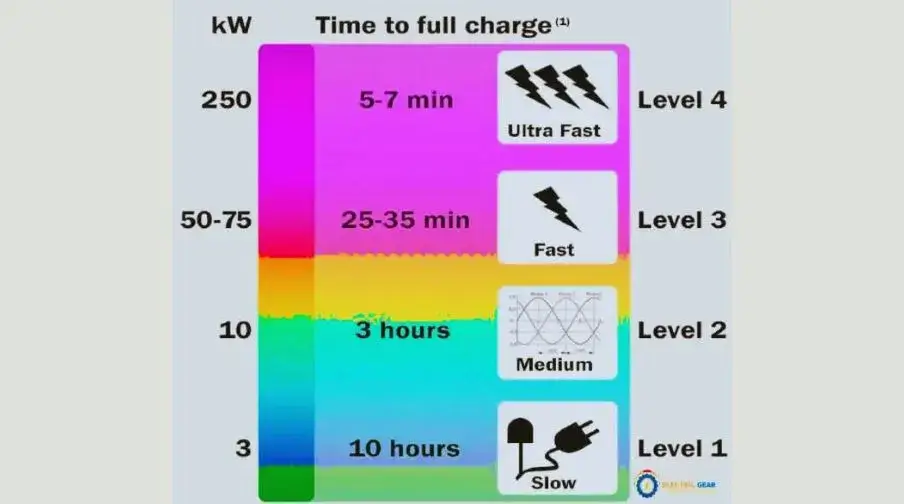
Level 1 Chargers
With a charging rate of around 2–5 miles of range per hour, level 1 chargers are the most basic kind of electric vehicle (EV) chargers. They are suitable for overnight charging at home or in quiet areas and usually use a standard 120-volt household outlet. It’s the least expensive and slowest charging option.
-
Level 2 Chargers
Higher-level charging stations, known as Level 2 chargers, can add between 10 and 30 miles to a battery’s range in just one hour. Public and private charging stations could provide the necessary 240-volt power supply. These chargers are great for high-traffic locations like businesses, shopping centers, and public parking garages where people need to charge their vehicles often.
-
DC Fast Chargers
DC Fast Chargers (Level 3 chargers) may add 60-80 miles to an electric car in 20-30 minutes. They use direct current (DC) electricity and require specific equipment found at highway charging points. Long-distance travel and fast charging require DC Fast Charges.
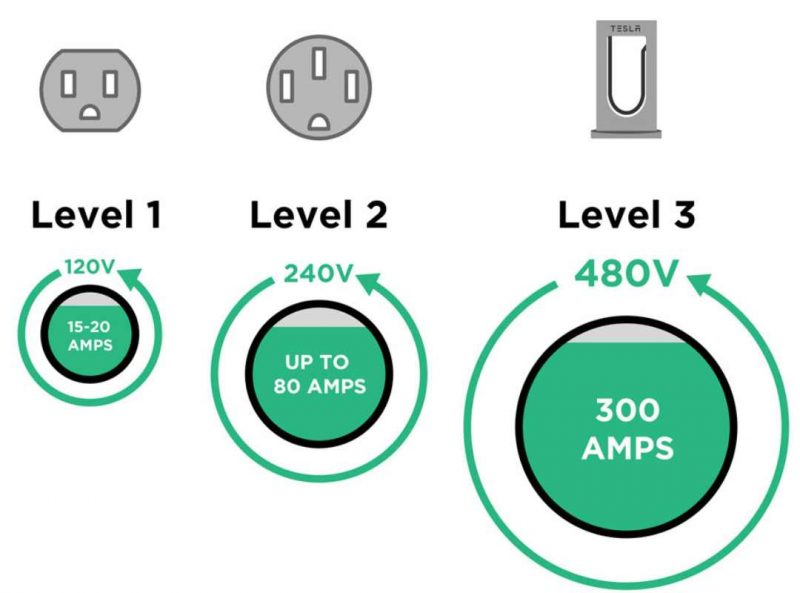
Charging Times for EVs by Different Chargers
-
Level 1 Charging Times
As electric vehicles (EVs) become more popular, it’s essential to understand the different charging options available. Level 1 charging, which uses a standard 120-volt household outlet, is the most basic and slowest option. The charging rate for Level 1 chargers is around 2-5 miles of range per hour of charging.
A full charge for an EV with a 60-mile range could take 12-15 hours. While Level 1 chargers are convenient for overnight charging at home, they may not be suitable for those with longer commutes or those who need quick charging solutions. Level 2 or DC Fast Chargers may be a better option.
-
Level 2 Charging Times
One of the primary worries of electric vehicle (EV) drivers is the length of time it takes to charge their vehicles fully. Level 2 charging stations, which may be found in many public and private locations, are significantly quicker and more convenient than Level 1 chargers. Level 2 charging typically takes between 4 and 8 hours.
However, this varies widely from battery size to charging station power. Now that more and more places provide Level 2 chargers, drivers of electric vehicles can charge their vehicles quickly and easily before hitting the road.
-
DC Fast Charging Times
Are you looking to charge your electric vehicle quickly and efficiently? Level DC fast chargers may be the solution you need. These chargers offer faster charging times than Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, which can charge some EVs up to 80% in as little as 30 minutes.
The exact charging time will vary based on your EV’s battery capacity, but DC fast charging can be an excellent option for those looking to top up on the go or complete longer journeys without lengthy charging stops. Plus, with more and more DC fast chargers installed nationwide, EV owners have greater access to fast charging options than ever.
Charging Time of Some Electric Vehicles
-
Charging Time of Tesla EVs

The time required to charge a Tesla electric car might vary depending on the charger type and model. With the particular Supercharger network offered by Tesla, you can get your Tesla battery up to 80 percent in less than half an hour.
While utilizing a Level 2 charger, it takes around 8.5 hours to charge a Tesla Model S or Model X fully. However, it only takes 8 hours to charge a Tesla Model 3 fully. Tesla’s newest car, the Model Y, has a charging time comparable to that of the Model 3.
Because of their user-friendly and effective quick-charging capabilities as well as their rapidly growing network of charge stations, Tesla electric vehicles (EVs) are in great demand.
-
Charging Time of Chevrolet Bolt EV
While utilizing a Level 2 charger, which can bring a completely depleted battery pack up to total capacity, the Chevy Bolt EV has a charging period of around 9.5 hours. It just takes sixty minutes for the Bolt EV’s DC fast charging system to get the battery up to 80 percent, making it a practical choice for extended road trips.
-
Charging Time of Kia EVs
The Niro and Soul EV are Kia’s electric car models. The Niro EV can be charged entirely in around 9.5 hours using a Level 2 charger, while the Soul EV needs about 9 hours.
Both versions may be charged up to 80%, with DC fast charging in about one hour. The range and charge time of Kia’s electric vehicle series is balanced, making them a sensible option for shorter commutes and longer trips.
-
Charging Time of Toyota EVs
The popularity of Toyota’s electric cars (EVs) is rising as more motorists want to lower their carbon impact. The charging time is a crucial aspect to consider when selecting an EV.
Toyota EV charging times might vary depending on the model, and the charging is done. For instance, a Level 2 charger can complete a full charge of the Toyota RAV4 Prime in as little as 2.5 hours, while a hydrogen gas fill-up of the Toyota Mirai fuel cell EV takes only 5 minutes.
No matter the model, Toyota is dedicated to offering its EV consumers safe and effective charging choices.
EV Charging Range Per Hour With Different Chargers
Here is a table format to summarize the charging range per hour with different chargers for electric vehicles:
| Charger Type | Power Supply | Charging Range Per Hour |
| Level 1 | 120V Household Outlet | 4-5 miles |
| Level 2 | 240V Outlet | 25-30 miles |
| DC Fast Charger | Public Charging Station | Up to 150 miles in 30 minutes |
Please be aware that the charging distance per hour may change depending on the kind of electric car and its battery capacity. Also, certain electric cars could not work with specific kinds of chargers. Always check the manufacturer’s instructions before charging your particular electric car.
Factors Affecting Charging Times
Here are some factors that can affect the charging time of electric vehicles (EVs):
- Battery Size: The size of the battery in an EV can affect the charging time, with larger batteries taking longer to charge. EV battery size is the primary factor that affects charging time. It will take longer to charge if its battery has a heavier pack (capacity measured in kWh). With a 7kW charging station, a standard electric vehicle’s 70 kWh battery takes 10 hours to recharge fully. The bigger the capacity of your EV, the more time it is likely to take to charge.
- Charging Method: The charging method can also affect the charging time, with Level 1 chargers taking the most extended and DC fast chargers being the fastest.
- Charging Rate: The charging rate of the charging station and the EV’s onboard charger can affect the charging time. The maximum charging rate of the charger you use for your vehicle limits how long it takes to charge a battery. For instance, even though your car has a charging capacity of 11 kW, a 7kW charger will only charge the battery for about 30 miles per hour.
- State of Charge: The current state of charge of the battery can also affect the charging time, with lower battery levels charging faster than higher ones.
- Temperature: The battery’s temperature can also affect the charging time, with colder temperatures slowing down the charging process.
- Charging Infrastructure: The availability and capacity of the charging infrastructure can also affect the charging time, with crowded or limited charging stations causing longer wait times.
- Driving Habits: The driving habits of the EV owner, such as frequent fast charging or driving at high speeds, can also affect the battery’s overall lifespan and charging time.
- State of battery: The state of the EV battery, nearly empty versus full, is also a factor in charging battery time. Charging almost empty batteries is also considered detrimental to battery health and takes more charging time.
- Maximum Charge Rate of the Car: Your EV battery is only charged at the highest charge rate if it can receive more power injected from the charger. For instance, some EVs are not designed to be charged from Level 3 fast chargers because they are incompatible with receiving direct current DC). Many electric vehicles can be charged up to 100 miles range in just 35 minutes while using a 50kW rapid charger. If your vehicle’s maximum charge rate is 7 kW, it won’t charge faster even with a 22 kW charger.
- Environmental Factors: Various physical and environmental factors can halt charging speed. The battery is more effective when maintained and charged under good atmospheric conditions.
If you are charging the vehicle under extreme atmospheric conditions of heat, cold, or immediately after driving, the charging rate would be slowed down. In cold climates, the battery tends to charge slowly.
Tips for Maximizing Charging Efficiency
With the ever-increasing popularity of EVs, it’s essential to know how to maximize EV charging efficiency. Here is a brief dropdown of some ways to get the most out of your EV charging:
1. Charge during off-peak hours: Charging your EV during off-peak hours can save you money on electricity bills. Off-peak hours are typically at night when the electricity demand is lower.
2. Use a Level 2 charger: Level 2 chargers are superior to Level 1 chargers in how rapidly and well they charge an EV. These chargers are more convenient since an electric vehicle may charge in only a few hours.
3. Avoid charging 100%: Charging your EV to 100% can reduce the battery’s lifespan. Charging your EV up to 80-90% is better to avoid overcharging it.
4. Monitor your EV’s battery temperature: Your electric vehicle’s performance may suffer if you charge the battery when it’s too hot or cold. Whenever possible, charge your EV while the battery is between 20 and 30 degrees Celsius.
5. Plan your route and charging stops: You may save time and lessen the likelihood of being stuck because of a dead battery if you plan your route and charging stations in advance.
By following these tips, you can maximize your EV charging efficiency and save time and money while ensuring your EV’s battery lasts longer.
Conclusion
In conclusion, maximizing EV charging efficiency is essential for EV owners to save time and money and ensure battery longevity. Charging during off-peak hours, using a Level 2 charger, avoiding charging to 100%, monitoring battery temperature, and planning your route and charging stops are some of the best practices to achieve this.
Following these tips, you can optimize your EV charging experience and enjoy all the benefits of driving an electric vehicle.