Hybrid vs Electric car! As environmental concerns continue to rise, more consumers are exploring eco-friendly transportation options, specifically hybrid and electric cars. It’s important to know the differences between these two kinds of vehicles to choose one that fits your life, budget, and environmental values.
This article will give you a clear comparison of both types of cars, covering how energy-efficient they are, how much they cost, how they perform, and how they impact the environment. This way, you can pick the best car for your needs.
Hybrid vs Electric car
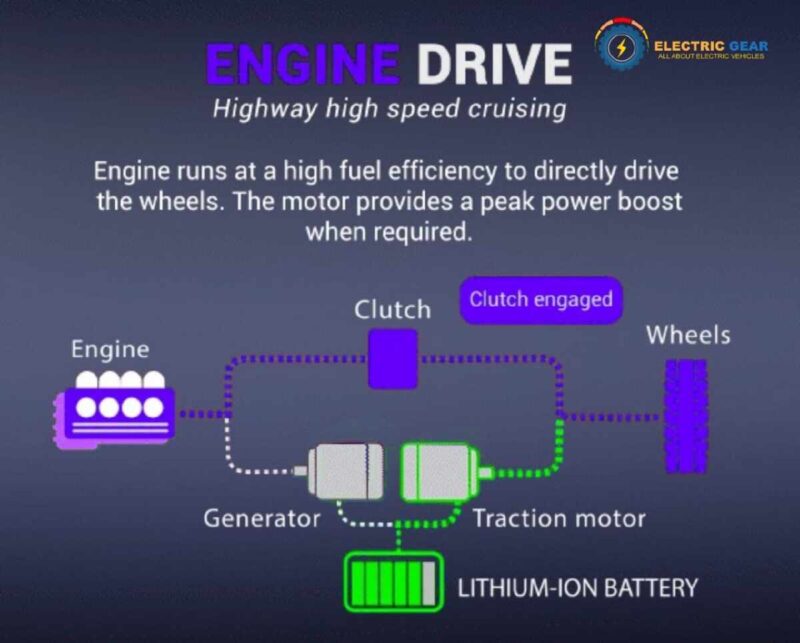
Hybrid cars have been around for decades but are still less popular than electric cars. Instead, hybrid vehicles are becoming less common than ever.
People often need clarification about hybrid and electric cars. Some think of both as the same, but there is a massive difference. If you consider any of these as your next vehicle, you must know the difference regarding the requirements and features.
Here, in this article, you will find how these are different. Let’s explore the differences between them.
What is a Hybrid Car?
Hybrid cars, or hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), combine a traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) with one or more electric motors. They use a gas engine and an electric motor either simultaneously or independently to maximize efficiency and minimize emissions.
The electric energy is stored in a high-voltage battery pack, which is significantly smaller than those in electric cars, and is charged through regenerative braking and the engine itself. Unlike electric vehicles, hybrids do not need to be plugged in to recharge.
Related: Types Of Batteries Used In Electric Vehicles
Key Components of a Hybrid Vehicle:
The following components are found in hybrid electric vehicles:
- Internal Combustion Engine
- Electric Motor(s)
- Electric Generator
- Battery Pack
- Fuel Tank and Filler
- DC Converter
- Thermal System
- Transmission
Advantages and disadvantages of hybrid vehicles
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Fuel efficiency on long trips | Higher initial purchase cost |
| Increased power | complex technology |
| lower emissions compared to gas-only vehicles. | higher insurance rates |
| reduced fuel economy in cold weather. |
Types of Hybrid Vehicles
- Parallel Hybrids: These are the most common type, where both the engine and electric motor can drive the car either separately or together.
- Series Hybrids: Only the electric motor drives the wheels, with the gasoline engine used to generate electricity for the motor.
- Plug-in Hybrids (PHEVs): These can be recharged by plugging into an external source of electric power and generally have larger batteries, allowing them to drive longer distances on electricity alone
What is an Electric Car?
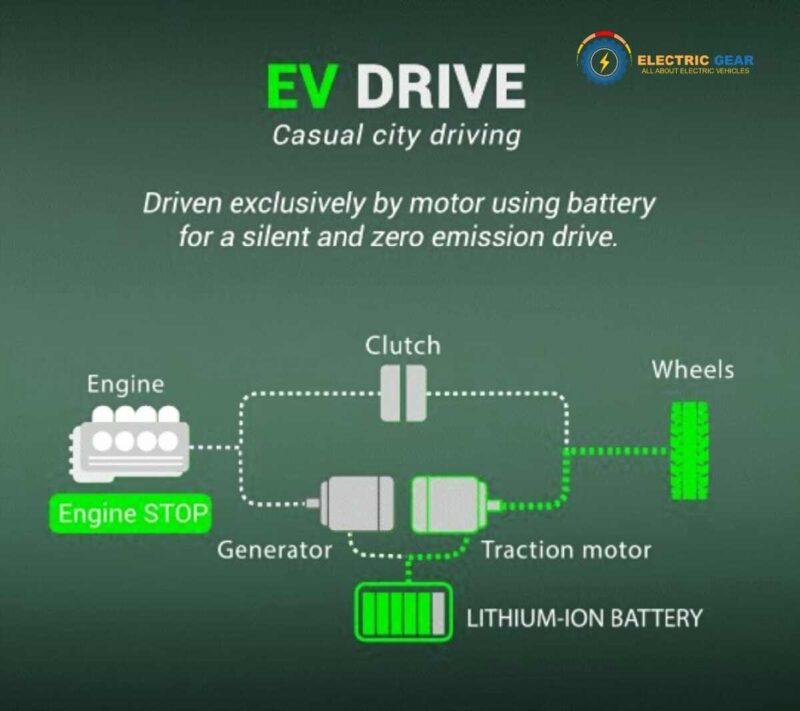
Electric cars, also known as battery electric vehicles (BEVs), operate entirely on electricity. They are powered by one or more electric motors that draw electricity from a large battery pack.
This battery is recharged by plugging into an external power source. Electric cars are known for having zero tailpipe emissions and a simpler mechanical design without the complex components found in gasoline-powered cars.
Key Components of an Electric Vehicle
- Electric Motor
- Large Battery Pack
- Power Inverter
- Onboard Charger
- Charging Port
- Transmission
- Thermal System
- DC Converter
Comparison of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles
Hybrid and electric vehicles, while having some similarities, do have some differences, which are mentioned as under:
| Comparison | Hybrid Cars | Electric Cars |
|---|---|---|
| Driving Range | Hybrids can typically travel as far as a conventional gasoline car. | offering 200-300 miles per charge, and some luxury models exceeding that. |
| Cost Considerations | Typically cost less than electric cars but more than conventional cars. | Higher initial costs, but prices are dropping as technology advances. |
| Incentives and Rebates | Can qualify for government incentives | Can qualify for government incentives |
| Emissions | Use gasoline, though significantly less than conventional cars. | Offer the potential for renewable energy integration, making them potentially more sustainable |
| Engines | Hybrids use both an ICE and electric motors | electric cars rely solely on electric power. |
| Charging | recharge their batteries through regenerative braking and the ICE | need to be plugged into a charging station. |
Related article: How do electric cars work? Absolutely oil free driving
Advantages and Disadvantages of HEVs vs EVs
- Purchase Cost: Electric vehicles can be more expensive upfront than hybrids, though prices are decreasing.
- Range: Modern EVs offer ranges that are increasingly competitive, often between 300-500 km on a full charge, but hybrids can still travel longer distances on a combination of fuel and electric power.
- Fuel Cost: Electric cars are cheaper to fuel with electricity costs averaging around $0.25 per kWh, making it about $4.50 to travel 100 km. Hybrids still rely on gasoline, which can be more expensive.
- Maintenance and Repair Costs: EVs generally have lower routine maintenance costs but may have higher repair costs due to the price of their parts.
Conclusion:
Choosing between a hybrid and an electric car depends on your specific needs and preferences. If you have reliable access to a charging station and are committed to reducing your carbon footprint, an electric car may be the best choice.
However, if you frequently travel long distances and are concerned about charging infrastructure, a hybrid could be more practical. Both options offer benefits for the environment and improvements in fuel efficiency over traditional gasoline vehicles, making them wise choices for the eco-conscious driver.
Frequently asked questions
What is the main difference between hybrid and electric cars?
Hybrid cars use a combination of an internal combustion engine and electric motors, whereas electric cars are powered solely by electric motors using energy stored in batteries.
Can electric cars be charged at home?
Yes, electric cars can be charged at home using a standard electrical outlet or a dedicated home charging unit, which provides faster charging speeds.
What is the range of an electric car on a full charge?
The range of an electric car can vary widely but typically falls between 150 to 300 miles on a full charge. Some newer models offer ranges that exceed 300 miles.
What are the environmental benefits of choosing an electric car over a hybrid?
Electric cars offer greater environmental benefits by producing zero tailpipe emissions, whereas hybrids, although better than traditional gasoline cars, still emit pollutants when running on gasoline.
How long do batteries last in electric and hybrid cars?
The lifespan of car batteries in both electric and hybrid vehicles can vary, but they typically last between 8 to 15 years depending on usage, with warranties often covering up to 8 years or a certain mileage.

Imran is an experienced content writer who crafts engaging and informative articles for a variety of industries. With a keen eye for detail and a passion for storytelling, Imran delivers high-quality content that resonates with readers. Whether he’s writing blog posts, social media content, or website copy, Imran is committed to delivering compelling content that drives results.







