Gas-only and electric vehicles use pretty different technology from each other. Powered by fossil fuel-burning internal combustion engines, gasoline-powered automobiles have been on the road for over a century.
On the other hand, electric vehicles’ power and speed come from electric motors and batteries.
As public awareness of global warming and air pollution risks has increased, so has the demand for electric vehicles. Both gas and electric cars have their benefits and drawbacks, so deciding between them depends on how often you drive, how much money you have, and your tastes.
Gas vs. Electric cars
EVs are considered superior because of their driving delicacy and environment-friendly features. Conventional vehicles, on the contrary, are more familiar to people, and they feel free to travel long distances with a single fill.
Electric vehicles (EVs) are gaining fame due to their reduced emissions, increased economy, and improved performance compared to conventional gasoline-powered automobiles.
Electric cars have fewer moving parts and are easier to maintain, but their batteries sometimes hamper their range.
Gasoline-powered vehicles may travel further, can be refueled more quickly, and are frequently less expensive overall, but they also produce more pollution and require more maintenance. Ultimately, one’s tastes, driving habits, and lifestyle demands determine whether one opts for petrol or electric.
However, the reservations regarding the EV’s various least-known features, like mileage and charging cost, will be mitigated with technological advancement.
When we talk about gas vs. electric cars, the latter has some advantages over gas-powered cars, but they, too, have downsides. Here we look at some pros and cons, including comparable and contradicting features.
Electric Cars vs. Gasoline Cars: Important Facts to Consider
When deciding between a gasoline-powered vehicle and an electric vehicle, there are a few aspects that are essential to take into consideration. It is important to keep in mind the following crucial points:
Fueling: Gasoline cars require regular refuel trips to the gas station, while electric vehicles can be charged at home or public charging stations.
Cost: Electric cars tend to have a higher upfront cost than gasoline cars, but they can be cheaper to operate over time due to lower fuel and maintenance costs.
Range: Electric cars typically have a shorter driving range than gasoline cars, although this is improving with advances in battery technology. However, it’s essential to consider your driving habits and how far you typically drive in a day before deciding.
Performance: Electric cars can have impressive acceleration and torque, making them fun to drive. However, some drivers may miss the sound and feel of a gasoline engine.
Environmental impact: Electric cars produce zero tailpipe emissions, making them a cleaner ecological option. On the other hand, gasoline cars emit pollutants that can contribute to air pollution and climate change.
Maintenance: Electric cars require less maintenance than gasoline cars, as they have fewer moving parts and don’t require oil changes. However, it’s essential to remember that electric vehicles have a high initial cost of maintenance if the battery needs to be replaced.
Gas vs electric cars: An analytical overview

Gas Vehicles
The most familiar type of vehicle today worldwide is the conventional vehicle using petrol, diesel, or gas as the primary energy source for internal combustion engines to make them move.
They have been around for a long time and are well known for their convenient drive, quick refueling, and traveling long distances between fill-ups.
Pros OF Gas Vehicles
Some of the significant features of ICE are given as follows:
Widespread prevalence: There are many filling stations worldwide, so it’s easy to find one and refuel a petrol car. It provides the buyer with more options as these have various vehicles.
Standard technology: Gas cars have been on the road for more than a century, so their technology is well-known by mechanics and drivers. They have a better driving range, convenient driving, and are likely to cause most minor problems for long distances.
Lower initial cost: Gas-powered vehicles often have a lower initial price than electric ones, making them more affordable for many consumers. They generally have higher top speed as compared to EVs. Typically, the Initial cost of purchasing a vehicle is cheaper.
Longer driving range: Gas-powered automobiles often have a more excellent range than electric ones, making them more convenient for lengthy drives and out-of-the-way locations. Technological advancements have made them more fuel efficient, thus covering more mileage with a single tank.
Fast refueling: Filling up a petrol tank usually takes a few minutes, but charging an electric car might take hours. Filling a gas tank and finding a fuel station is more easily accessible than charging your EV.
CONS OF GAS VEHICLES
Environmental concerns: Electric cars are better for the environment since petrol cars produce pollution and worsen global warming. Frequently contribute leftover oil, toxic waste, and harmful fluids into the environment. It badly affects the environment in more ways than one.
Fuel prices: Energy prices are challenging to forecast, making it difficult for drivers to plan for these expenses.
Repair and maintenance: Gas-only vehicle servicing is more time-consuming and costly for gas-powered automobiles due to the complexity of their engines. Engine and transmission oil changes and coolant are the periodic requirements.
Noise pollution: Gas-powered vehicles contribute more to urban noise pollution than their electric counterparts.
Limited energy efficiency: The energy from gasoline is mainly wasted as heat and pollutants in petrol cars, making them less efficient than electric vehicles.
Advantages of Electric Vehicles

Environment concerns: Compared to gas-powered vehicles, electric ones produce far less pollution in the form of carbon dioxide.
Lower operating costs: Electric vehicles have lower operating expenses than gasoline vehicles since they use less fuel and require less maintenance because of their simpler drivetrains.
Performance: Electric vehicles provide a more comfortable and responsive driving experience because of their immediate torque and smoother acceleration.
EVs have fewer moving parts resulting in less wear and tear. They need no periodic oil changes and no routine tune-ups. Electric vehicles have high performance, the least energy is wasted, the drive is smooth, and the low Cost Per Kilometer contributes to cleaner energy.
Energy security: Powering electric cars with electricity helps to diversify the country’s energy supply and lessen its reliance on imported oil.
Cutting-edge features: Regenerative braking, smart charging, and energy monitoring are just a few of the cutting-edge technologies that are becoming standard on electric vehicles.
Charging at home: Convenient and inexpensive recharging alternatives are available to owners of electric vehicles thanks to the ability to charge their cars at home using a regular outlet or quicker charging stations. One can charge the battery at home. So you don’t need to go far off gas stations.
Maximum torque (power) even at 0 RPM: Electric vehicles (EVs) have a distinct advantage over internal combustion engine vehicles in that they can produce maximum torque or power even at 0 RPM.
This means EVs can accelerate quickly from a standstill, making them a popular choice for performance-oriented vehicles.
Govt incentives: The government’s various EV incentives help save money.
Disadvantages of EVs
Limited driving range: Because they need to be recharged more often, electric vehicles aren’t ideal for long trips because of their limited driving range compared to gas-powered vehicles.
Limited charging infrastructure: Restricted charging infrastructure in some locations makes long-distance travel challenging for owners of electric vehicles.
The higher initial cost: The higher upfront cost of an electric car may be offset by the lower running costs experienced by the owner throughout the vehicle’s lifetime.
Longer charging time: Charging takes a considerably long time, but fast-charging stations can help reduce the time it takes to recharge an electric car compared to a gas-powered vehicle. It wastes time while charging on the way and takes at least 1 hour.
Battery lifespan and costly replacement: The cost and inconvenience of replacing the battery in an electric car might cut into its resale value and reduce its useful life. The battery loses power over time. The need may arise to replace the expensive battery almost every ten years.
- Battery range: EV batteries tend to lose range over time.
- EV production produces emissions: Electric vehicles, like gas vehicles, typically come with emissions.
- They are not fit for daily use, and their repair cost is high.
Driving Difference Between Gas vs. Electric Cars
There are multiple considerable distinctions between gas and electric automobile driving.
Gas automobiles are best suited for extended, high-performance journeys because of their greater power and extended driving range. Petrol engines are often louder, less smooth, and more prone to breakdowns than electric motors.
On the other hand, The instantaneous torque and quiet, smooth ride of an electric automobile are only two of its many advantages. The overall difference between the gas-only and electric automobile driving experiences might depend on the driver’s preferences and driving habits.
Shifting From Conventional to Electric
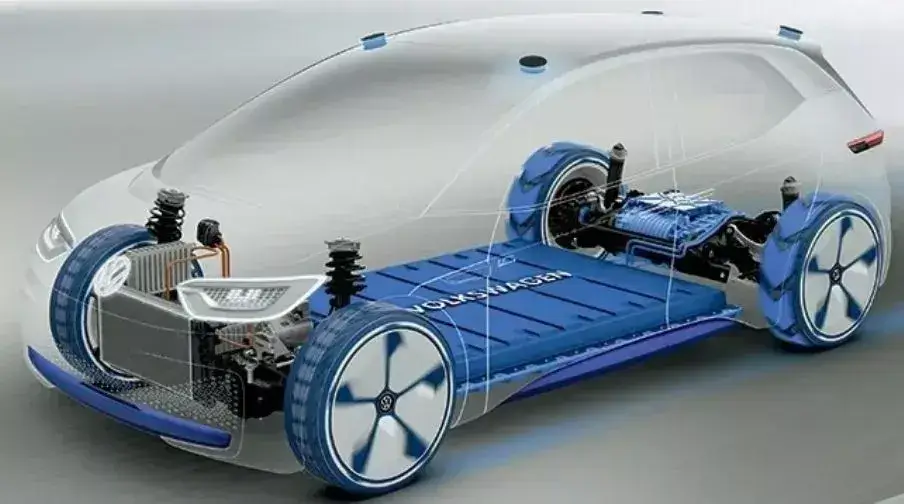

The process of shifting from conventional to electrical is evolutionary, and people’s grave concerns regarding EV’s mileage, battery lifetime, and initial cost have long hindered going electric.
However, technological enhancements have improved these EV features to their optimal strength compared to the recent past. In today’s world, concerns for emissions, cleaner earth, gas prices, and other factors drive people to go electric.
People are now considering replacing their vehicles with EVs. Due to this increasing trend worldwide —most countries —including the USA, are planning to impose a complete ban on buying gasoline vehicles during the next decade or so.
While switching from a gas-powered car to an electric one has advantages, it may also need changes to one’s driving habits and the surrounding infrastructure. To help with the transition, here are some suggestions:
Evaluate Your Driving Requirements: Think about how often you drive, how far you usually go, and how easy it would be to find a place to plug in an electric car.
Do your homework on the EV market: Compare several models based on criteria like range, charging time, and price to locate the one that best suits your demands and budget.
Upgrade your home charging system: Installing a charging station can make charging your electric car at home easier.
Adjusting driving habits: Make a change to your driving habits to increase your electric vehicle’s range by using regenerative braking and avoiding aggressive driving.
Plan for long travels: Plan your travel by marking charging outlets along the way and being patient, as charging takes longer than refilling with petrol.
Aware of EV incentives: Tax credits and refunds are only two examples of the incentives offered by several governments and regions to encourage the purchase of electric vehicles.
Learn EV maintenance: To get the most out of your EV and keep it running smoothly and reliably for as long as possible, you should acquaint yourself with its unique maintenance needs.
Do electric cars take gas?
Battery power is the only energy source in EVs for the electric motor, which propels and provides the necessary power to move the wheels. The battery is charged through an external outlet or a regenerative braking system.
Final Thoughts
Before going electric, you must review all the relevant concerns regarding charging infrastructure, driving viability, initial cost, etc. Delays in deploying these green-house reducing models are the want of charging stations and coordination across inter-government levels.
Both petrol and electric automobiles have their benefits and drawbacks, and several circumstances influence the decision between them.
Electric vehicles are more cost-effective and produce less pollution, while gas-powered cars can go further between fill-ups. This divide will be narrowed as both technology and Electric infrastructure improve.
The final decision between a petrol and electric vehicle will be based on the buyer’s tastes, driving habits, and environmental concerns.
If going eco-friendly is always necessary, considering the stable climate effects, an EV might be the vehicle you sought.

Imran is an experienced content writer who crafts engaging and informative articles for a variety of industries. With a keen eye for detail and a passion for storytelling, Imran delivers high-quality content that resonates with readers. Whether he’s writing blog posts, social media content, or website copy, Imran is committed to delivering compelling content that drives results.