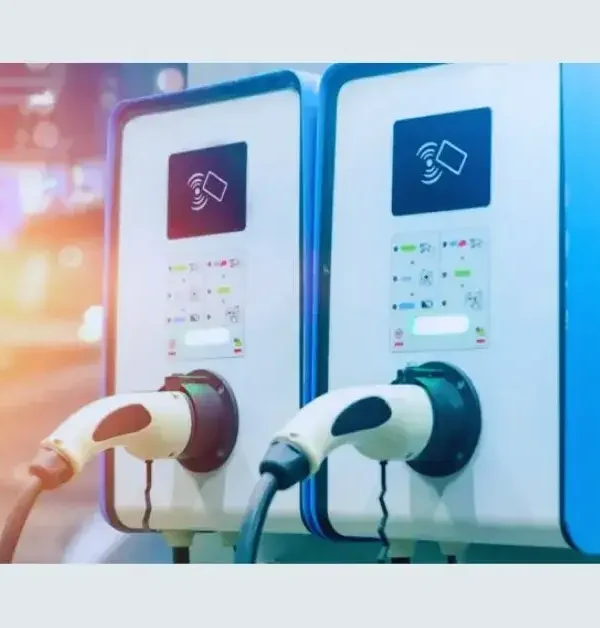
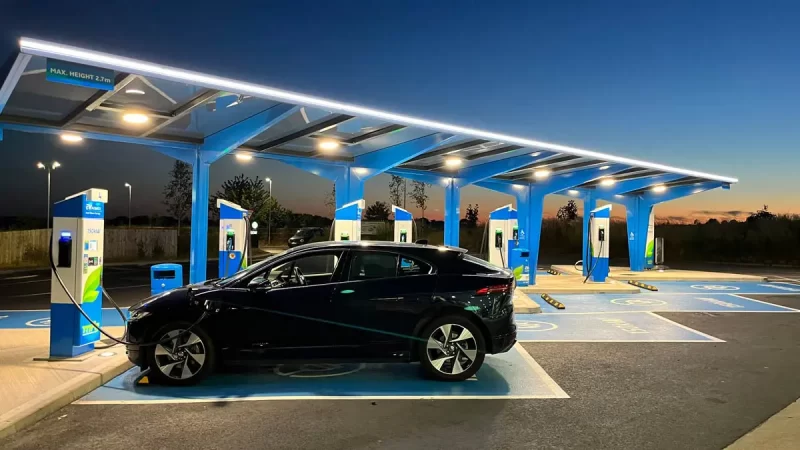
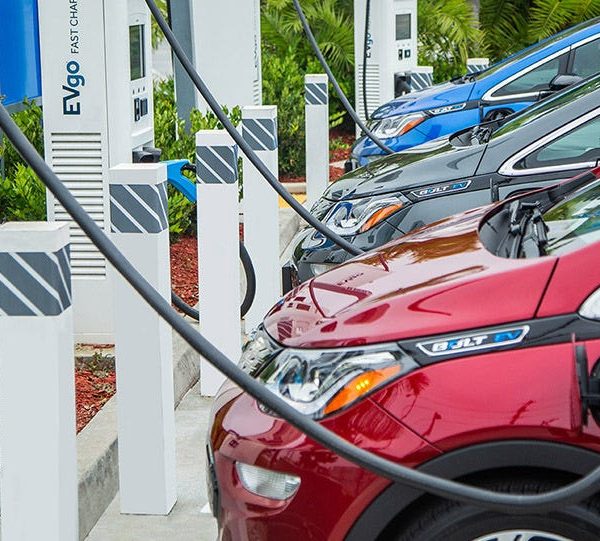
Level 3 DC fast charger converts AC into DC within the charging station, providing DC electric power to charge the battery and enabling the fastest EV charging.
However, the charging speed of the Level 3 DC fast charger depends on multiple factors, including the battery’s capacity to receive power, the charger’s power level, and the battery’s remaining percentage of charging.
According to a report by the Department of Energy, more than 15% of EV charging stations in the US are Level 3 DC fast chargers.
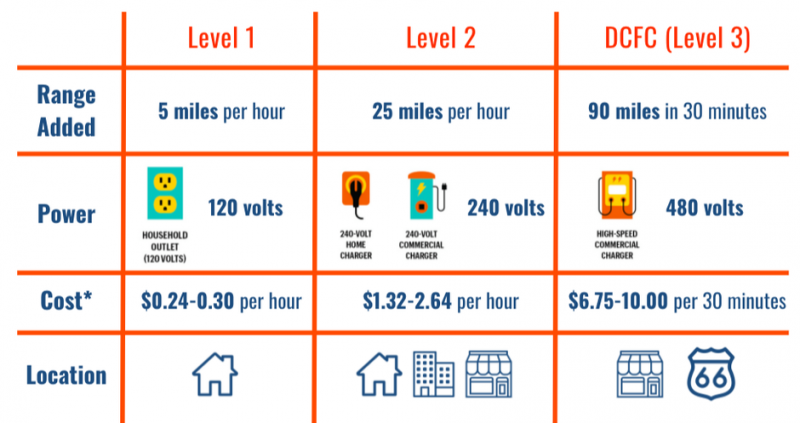
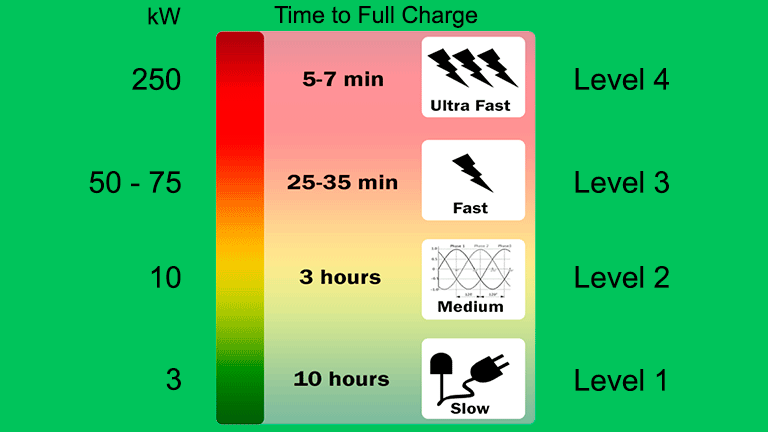
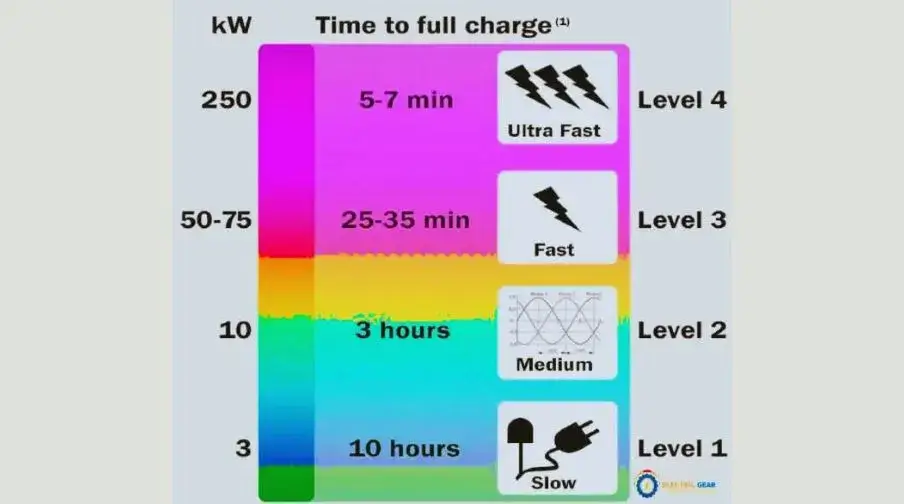
Level 3 DC fast chargers or superfast chargers can charge an EV battery at a quicker speed of 3 to 20 miles per minute. It is, in fact,16 to 30 times faster than a level 2 charger and takes almost 30 minutes to charge the battery fully.
People now worldwide are more familiar with traditional vehicles and their charging trends. They have limited options at the gas stations, and the refueling process is simple, it hardly takes a few minutes for a domestic vehicle to refill.
The process of refueling (recharging) EVs is still rare and is somewhat complicated to the extent that most people need clarification about the charging process and method.
It is so because EVs are new in most parts of the world, and secondly, most EVs come with different charging variations using different levels of charging stations and connectors.
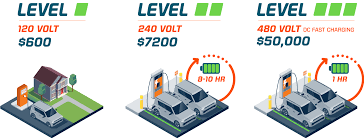
What is a Level 3 DC charging station? 400-volts – 950-volts
The superfast charger, or the Level 3 DC fast charger, is the quickest charging system capable of charging at an alarming rate of approximately 3 to 20 miles per minute. It uses direct current(DC), unlike Level 1 or 2 charging stations, which use alternating current(AC).
Level 3 chargers have the highest voltage range than Level 1 and 2, and you can not put a Level 3 charger at home. Hence, it requires a controlled environment and a vast voltage supply.
Various charging levels have been introduced to fulfill the ever-emerging demand of EV owners across the globe. DC fast chargers can provide power from 200 to nearly 900 DC voltage, also known as Level 3 chargers.
They are used for high-access public areas, public transportation, and large commercial vehicles and can charge EV batteries in less than 30 minutes.
Installation of Level 3 DC Supercharger
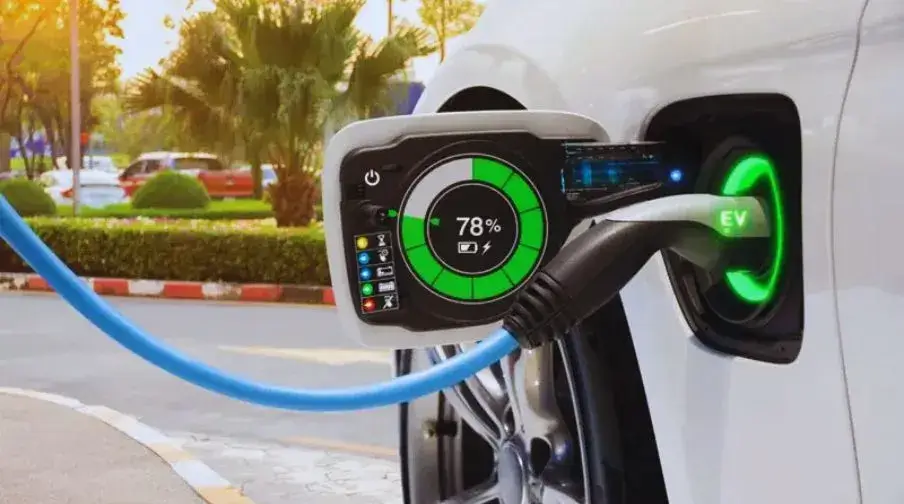

Level 3 DC fast chargers have the highest voltage of up to 900 DC volts and, thus, require an extra high level of skill, highly secure infrastructure, and a proper system to maintain these voltages.
These charging stations are installed in high-access public areas for EVs, public transport, and large commercial vehicles.
Some people think of installing Level 3 superchargers at home, but they must keep in mind that the cost of doing so may exceed tens of thousands of dollars, and in some cases, it will surpass the price of the EV you own.
Furthermore, only a few residential locations may have the supply of such high-voltage required to install and supply power to Level 3 DC fast chargers.
If it can be, in any case, fitted at home, it will require a skilled person to operate and maintain it in the long run.
However, installing these enormously high-voltage Level 3 chargers requires technical infrastructure and skilled labor.
Cost to Install Level 3 DC Fast Charger
Many factors affect how much it will cost to install a Level 3 DC fast charger, including the site’s accessibility, the charger’s power output, and any required electrical infrastructure changes. Putting up a Level 3 charger can be expensive, typically costing $10,000 to $50,000 or more.
Most of the budget goes into the charger itself, which can cost $20,000 to $40,000 or more for more powerful Level 3 chargers. In addition to the charger’s price, additional fees may be associated with installation if additional wiring is required to meet the device’s power needs.
There may also be expenses for things like site studies, permits, and other forms of government monitoring. Level 3 chargers can be expensive to install, but certain businesses may qualify for subsidies or incentives from government programs or utility providers to help cover the expense.
Requirements for Installing Level 3 Charger
Installing a level 3 DC fast charger requires careful planning and consideration of several requirements to ensure its safe and efficient operation. Here are some of the essential requirements:
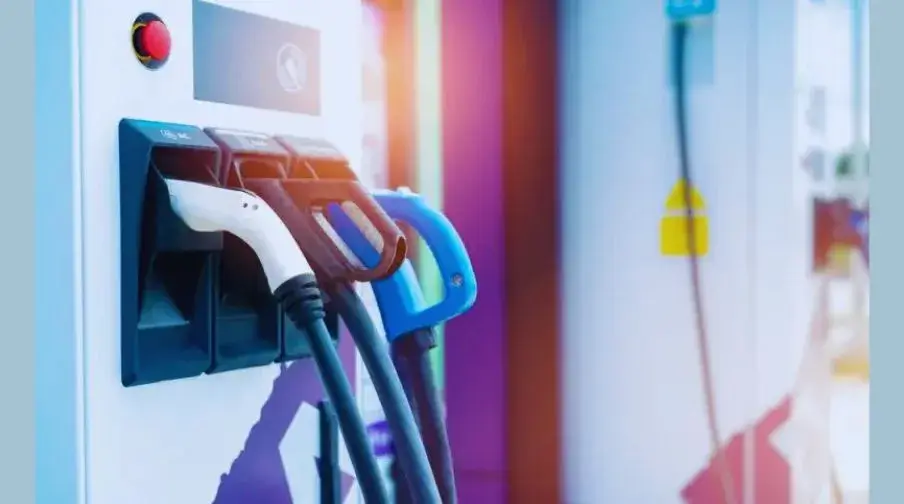

- Power supply: A level 3 DC fast charger requires a direct high-voltage current (DC) power supply. The power supply should deliver at least 50 kilowatts (kW) of power to the charger.
- Electrical infrastructure: The electrical infrastructure should be able to handle the load of the DC fast charger. This includes the leading electrical service, substation transformer, and distribution panel.
- Site requirements: The site should have enough space to accommodate the DC fast charger and the associated electrical equipment. The site should also have proper drainage and should be level and stable.
- Environmental factors: The DC fast charger should be installed in a suitable location protected from elements like rain, snow, and extreme temperatures. It should also be located away from flammable materials and hazardous areas.
- Safety requirements: Installing a level 3 DC fast charger should comply with all applicable safety standards and regulations. This includes grounding, bonding, and other safety measures.
- Communication and networking: A level 3 DC fast charger requires a remote monitoring and control communication network. It includes an Ethernet connection, cellular network, or Wi-Fi connection.
- Accessibility: The DC fast charger should be accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. It includes appropriate signage, accessible parking, and a clear path of travel to the charger.
It’s crucial to consult with a professional electrician and obtain the necessary permits and approvals from the local authorities before installing a level 3 DC fast charger.
DC Fast Chargers – Way to Boost Business
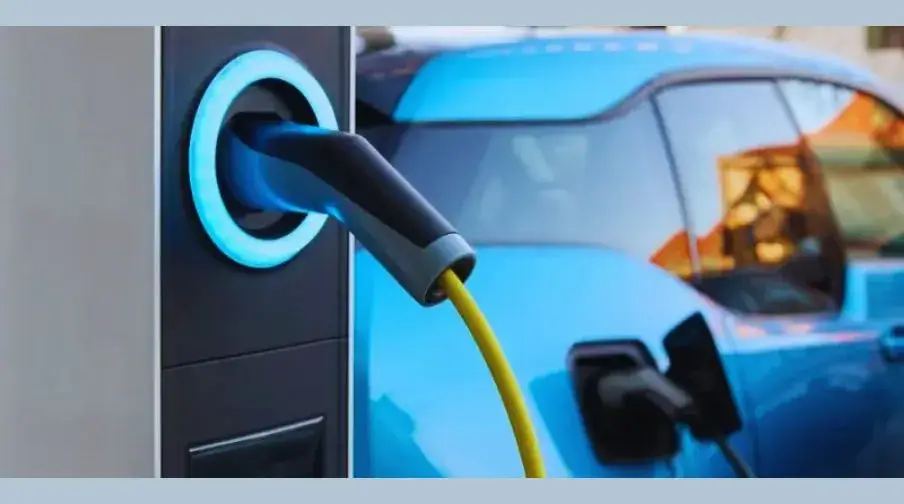

In countries like the USA, Canada, U.K., where the EV industry is growing at an accelerated pace, the idea of installing a Level 3 fast charger is unique. It can significantly assist financially, as a Level 3 DC fast charger reduces downtime exceedingly.
EVs are now seen in much more quantities than ever across the globe, and lacking the facility of fast charging is still considered a hurdle for some people willing to go electric because they want to save time.
Large commercial vehicles must also be recharged soon, so it’s time to go for DC fast chargers far and wide the globe. Traditional fuel costs are going higher and higher by the day, and the prediction of the depletion of fossil fuels can be heard all around.
Furthermore, the differences in prices between the two are substantial, and by going electric and saving money, your vehicle becomes eco-friendly.
How fast is a Level 3 charger
A Level 3, or a DC fast charger, is a high-powered charging station designed to charge electric vehicles (EVs) much faster than Level 1 or Level 2 chargers. Although Level 1 and Level 2 chargers utilize alternating current (AC), Level 3 chargers use direct current (DC) to charge an EV’s battery (AC) quickly.
A Level 3 charger’s charging rate can change based on the EV and the charger’s power output. Yet, most Level 3 chargers can fill the battery of an average EV with up to 80% of its capacity in roughly 30 minutes.
Some powerful Level 3 chargers can even supply a complete charge in less than an hour. Level 3 chargers are, therefore, perfect for usage at public charging stations, where EV vehicles may need a quick recharge.
RTM is considered to be the fastest Level 3 charger available. It can charge an EV battery in just minutes instead of Levels 2 and 1, which take hours. Level 3 fast chargers charge the battery 180-1200 miles an hour.
Do all EVs support a level 3 Charging system?
A small fraction of plug-in-hybrid and electric vehicles are not fit for charging on Level 3 chargers because different vehicles have different battery powers and, thus, accept an additional amount of electricity.

Vehicles with small battery packs are incompatible with consuming vast amounts of energy from fast chargers. Additionally, EVs usually use AC charging, and to avail of a DC fast charger facility, a vehicle must support the DC charging system.
Features of Level 3 or Superchargers
- It charges most of the EVs and plug-in-hybrid. However, the least quantity of EVs is excluded from it.
- Level 3 DC fast charger can charge 3-20 miles per minute.
- It can charge 0% to 80% in less than 30 minutes.
- DC fast charger provides AC and DC charging simultaneously.
Can All EVs be Charged on a Tesla Supercharger?
No, only Tesla electric vehicles are compatible with Tesla Superchargers, and level 3 DC fast chargers can only be used to charge Tesla electric vehicles. Tesla Supercharger networks are a proprietary asset of Tesla, and Tesla uses this facility to facilitate its customers only.