In the world of car technology, electric vehicles (EVs) have become an important answer to increasing environmental concerns and the need for better energy use. There are different types of electric cars available, each with its way of working and benefits.
These include Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs), Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs), Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), and Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs). (Mild Hybrid Electric Vehicles (MHEVs) and Solar Electric Vehicles (Solar EVs) are not as common and can be covered in a separate discussion.)
This article will help explain these types, how they work, their advantages and disadvantages, and what makes each of them unique, helping consumers make informed choices as technology continues to evolve.

Introduction to Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles, or EVs, are a new kind of car that uses electricity instead of gasoline to run. This change is good for the environment because it means less air pollution. It can also save money since electricity can be cheaper than gas.
Types of EVs
Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
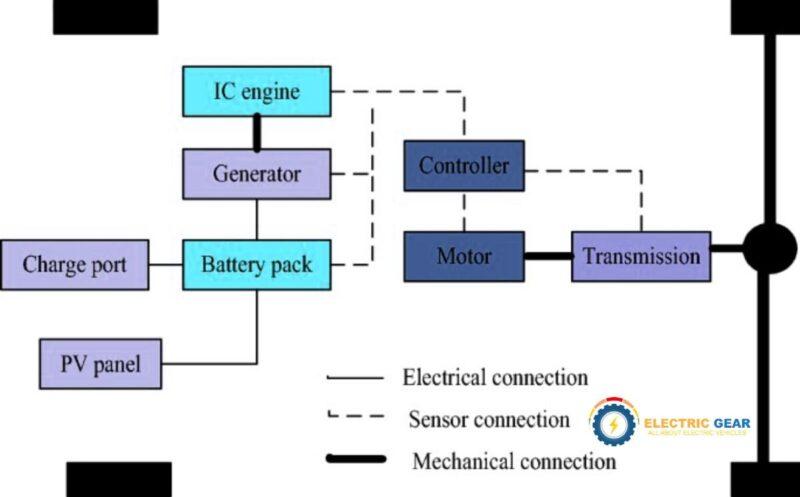
Hybrid Electric Vehicles, or HEVs, are a combination of traditional gasoline-powered engines and electric motors. These types of cars are often called hybrid cars. They have a gasoline engine and one or more electric motors that help power the car.
The electric motors get their energy from a type of battery called nickel-metal hydride (NiMH). This battery gets recharged by a process called regenerative braking, which turns the energy created when the car slows down into electricity.
How They Work:
In HEVs, the electric motor can run the car on its own for short distances at low speeds. After this, the gasoline engine kicks in. This setup helps save fuel and cuts down on pollution when the car is starting up or moving slowly. For faster speeds or longer trips, the gasoline engine provides the necessary power.
Read more:
Do electric cars have catalytic converters? A detailed Guide
Basic Working Principles of HEVs
Dual Power Sources: HEVs have two main components for propulsion: an internal combustion engine (ICE) and one or more electric motors. The vehicle can switch between these power sources or use them simultaneously based on driving conditions.
Energy Storage: The electric motor is powered by a battery, typically a nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) or lithium-ion battery. This battery stores electrical energy that powers the electric motor.
Regenerative Braking: One of the key features of HEVs is regenerative braking. When the vehicle slows down or stops, the electric motor works as a generator, converting some of the kinetic energy (movement energy) that would otherwise be lost into electrical energy. This energy is then stored in the battery. This process helps to recharge the battery without needing an external power source.
Automatic Start/Stop: HEVs can automatically turn off the ICE when the vehicle is idling and restart it when needed (such as when accelerating). This reduces idle time and saves fuel.
Electric Motor Assistance: During acceleration, the electric motor can assist the gasoline engine, providing additional power. This helps the HEV to use less fuel and emit fewer exhaust gases compared to traditional gasoline vehicles.
Optimized Engine Load: The hybrid system can optimize the load on the gasoline engine, allowing it to operate at an efficient rate more often. This minimizes the inefficient fuel consumption and emissions that occur when gasoline engines operate under varying loads.
Examples of HEVs
- Toyota Prius
- Toyota Camry
- Volvo XC90
- Lexus NX
- Chevrolet Tahoe Hybrid
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Cheaper than BEVs or PHEVs. | On most models, the mileage range is minimal. |
| HEVs are environmentally friendly. | As compared to BEVs, tax benefits are minimal. |
| Use less gas as compared to a conventional vehicle. | Depending on the driving circumstances, the fuel economy advantages can change. |
| They are quiet. | Their upfront cost is higher. |
| Auxiliary devices can be powered by electric components, improving acceleration. | HEVs have comparatively less power if compared to standard ICE. |
| These do not eliminate harmful emissions. |
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
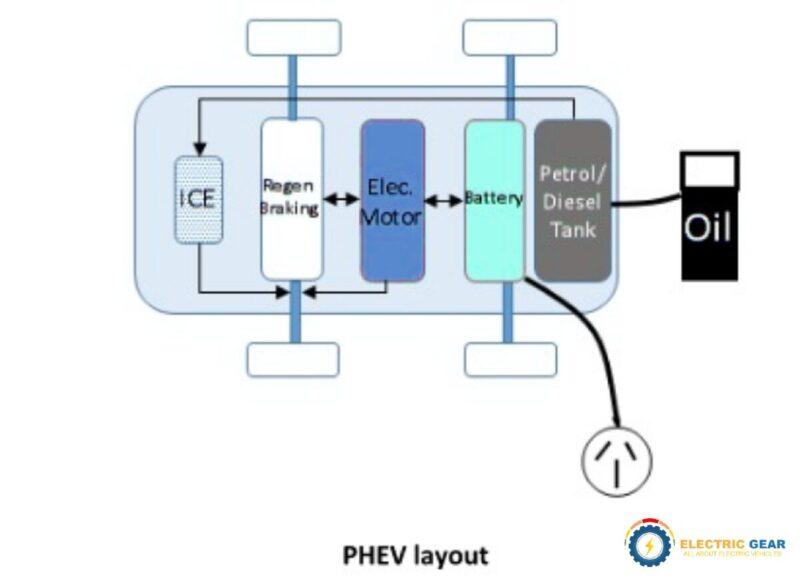
PHEVs function similarly to HEVs but with the added capability to recharge their batteries through external electrical sources. This feature allows them to drive significant distances on electric power alone. Like hybrid, based on driving conditions, it switches between ICE (Internal Combustion Engine) and electric mode.
How They Work
PHEVs have larger batteries than HEVs, which can be charged via standard electrical outlets or charging stations. This enables them to operate in all-electric mode for distances of 20-70 miles, after which the gasoline engine can extend its range, functioning much like an HEV.
Examples of PHEVs
- Tesla Model 3
- Tesla Model x
- BMW i3
- Nissan Leaf
- Chevy Bolt
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Less costly than BEVs. | Expensive than a petrol-powered vehicle. |
| Only partially dependent on battery capacity and infrastructure for charging. | Any cost savings will be lost if the battery is not charged. |
| If the routine trip is short, you can drive primarily on battery. | Running costs may rise with more complexity. |
Basic Working Principles of PHEVs
Dual Power Sources: Like HEVs, PHEVs have two main sources of power: an internal combustion engine (ICE) and one or more electric motors. What sets PHEVs apart is their ability to operate on electric power alone for longer distances, thanks to larger battery packs.
Plug-in Capability: PHEVs are equipped with a larger battery pack that can be charged by plugging into an external electric power source, such as home chargers or public charging stations. This feature allows PHEVs to drive significant distances on electricity alone, reducing fuel consumption and emissions when the battery is charged.
Regenerative Braking: PHEVs also utilize regenerative braking to convert kinetic energy from braking into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery. This process helps recharge the battery while driving and reduces the need for traditional braking, which in turn reduces wear and tear.
Electric-Only Mode: PHEVs can operate in an all-electric mode, using only the electric motor for propulsion, which results in zero fuel consumption and emissions. The distance they can travel in this mode depends on the battery’s capacity and can range from about 20 to 50 miles or more.
Hybrid Mode: When the battery’s charge is depleted, PHEVs switch to hybrid mode, where both the electric motor and the gasoline engine are used. The vehicle automatically manages the use of the electric motor and gasoline engine to optimize fuel efficiency and performance, similar to HEVs.
Automatic Start/Stop: This feature is also present in PHEVs. The gasoline engine can shut off when the vehicle is stopped (e.g., at traffic lights) and restart when acceleration is needed, which conserves fuel and reduces emissions.
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
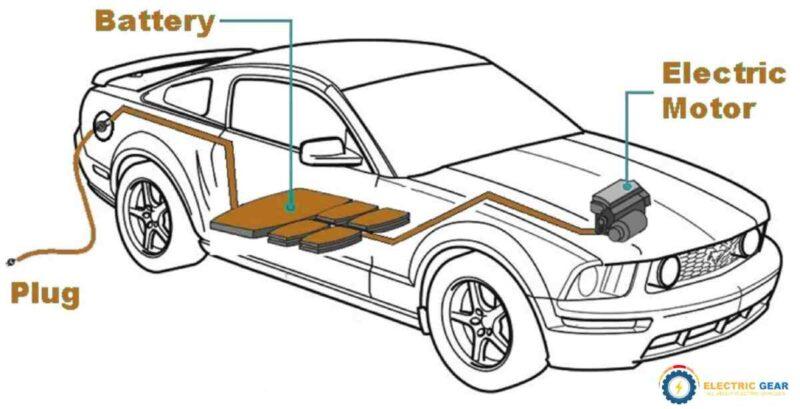
BEVs represent the purest form of electric vehicles, relying solely on electric power from batteries, without any form of conventional gasoline engine.
How They Work
These vehicles are equipped with large battery packs that power an electric motor. BEVs require regular charging from external sources but offer the benefit of completely emission-free driving.
Examples of BEVs
- Tesla Model Y
- Tesla Model 3
- Nissan Note
- Ford Focus
- Hyundai Ioniq
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Excellent performance. | Compared to filing a tank, charging takes longer and is less convenient. |
| The cost of maintenance is low beyond changing tires and windshield wipers. | Not known as ideal for longer distances due to limited battery power. |
| Less loss is expected as fewer moving parts. Even the brakes don’t degrade sooner due to the regenerative braking system. | Prices are typically higher than regular cars. |
| Far quieter than any other. | The driving range is less than that of gasoline vehicles. |
| EVs are tailpipe emission-free. | The cost of insurance might be increased. |
| It runs on electricity, which costs less than gasoline. | The initial purchase cost is higher. |
| Easy to drive with no gear changes. | Replacement of battery (however rare) is expensive. |
Mild Hybrid Electric Vehicles (MHEVs)
MHEVs are similar to HEVs but with a smaller battery and electric motor. These vehicles cannot be driven on electric power alone; instead, the electric motor assists the ICE, particularly during acceleration.
How They Work
The electric motor in MHEVs supports the engine, reducing the overall fuel consumption and emissions. The battery is charged through regenerative braking, similar to HEVs.
Basic Working Principles of MHEVs
Integrated Starter Generator (ISG): MHEVs typically incorporate an Integrated Starter Generator, which replaces the conventional starter motor and alternator. The ISG serves multiple roles: it starts the engine, generates electricity, and provides additional power to assist the engine during acceleration.
Electric Motor Assistance: The electric motor in MHEVs assists the internal combustion engine (ICE) by providing additional power when needed, such as during acceleration or hill climbing. This assistance helps to reduce the load on the engine and can lead to lower fuel consumption and emissions.
Energy Recovery System: MHEVs utilize regenerative braking similar to other hybrids. When the vehicle brakes, the ISG functions as a generator to recover kinetic energy (the energy of motion) and convert it into electrical energy. This energy is then stored in a small battery.
Battery: MHEVs are equipped with a smaller battery compared to PHEVs and BEVs. This battery is not designed to power the car on its own; instead, it stores energy captured during braking and powers the electrical systems and the ISG.
Stop-Start System: One of the most noticeable features of MHEVs is an advanced stop-start system. When the vehicle comes to a stop, such as at a traffic lights, the engine can shut off completely to save fuel. As soon as the driver presses the accelerator, the ISG quickly restarts the engine.
Electric Boost: The electric motor in MHEVs can provide a ‘boost’ of power to the engine during heavy load conditions, helping to improve acceleration without significantly increasing fuel consumption.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Compared to conventional vehicles, it has a smoother stop or starts function. | Limited Performance Enhancement |
| Accelerate more quickly. | Small Battery Size |
| Use less fuel than gasoline-powered cars. | Dependence on Engine for Charging |
| Driving in purely electric mode is not possible. | No Electric-Only Driving |
| There is no substantial tax benefit. | Incremental Cost Increase |
Related Article:
Electric vehicle maintenance: 10 best methods to keep EVs
Solar Electric Vehicles (Solar EVs)
Solar electric vehicles (Solar EVs) are a cool kind of electric car that uses the sun’s energy to run. They have solar panels on the roof that turn sunlight into electricity. This electricity charges the car’s batteries and powers the motor.
How Do They Work?
Solar EVs use something called photovoltaic cells in their solar panels to catch sunlight and turn it into electricity. This can be used right away to drive the car or stored in the battery for later. Being able to use sunlight helps these cars go farther without needing to stop for a charge, and it’s great for the environment.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| These cars don't emit any pollution | There's a limit to how much electricity they can make. |
| They can make their own electricity from sunlight | Their performance can go down on cloudy days or at night |
| Using the sun's energy helps reduce the need for fossil fuels, making these vehicles super sustainable. | The technology needed to blend solar panels into cars can make them more expensive at the start. |
Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs)
Fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) generate electricity through a cool chemical reaction between hydrogen gas and oxygen from the air. This powers the car’s motor. The only thing these cars emit from their tailpipe is water vapor, making them super clean.
How Do They Work?
In FCEVs, hydrogen gas is pushed into a fuel cell where it meets oxygen. This meeting produces electricity, which drives the car’s motor. Any extra power gets stored in a battery, similar to hybrid cars.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| These cars are incredibly clean. | There aren’t many hydrogen stations yet, which makes it hard for these cars to be practical everywhere. |
| You can fill up the hydrogen tank as quickly as you would a regular gas tank | Making hydrogen and building fuel cells is still expensive, which can make these cars pricier than other types. |
| FCEVs can go as far as traditional cars on a full tank, making them a great option for long trips. | Making hydrogen in a way that’s totally clean can be challenging. If it’s not done right, it could offset some of the environmental benefits. |
Conclusion:
Electric vehicles come in many types, each suited to different needs and preferences. You’ve got BEVs, which are fully electric cars, HEVs and PHEVs that combine electric power with gasoline engines, and MHEVs that offer a little electric boost to help the engine.
As car technology gets better and charging stations become more common, more people are expected to choose electric cars. This shift will help make the car industry more environmentally friendly and efficient, leading us toward a future where transportation does less harm to the planet.
Frequently asked questions
How do extended-range electric vehicles (EREVs) work?
Extended-Range Electric Vehicles (EREVs) are a type of PHEV that uses its gasoline engine primarily to generate electricity for the electric motor, rather than directly powering the wheels. This allows for longer electric-only driving capability compared to typical PHEVs.
What is the difference between an electric vehicle and an electrically assisted vehicle?
An electric vehicle, such as a BEV, uses only electric motors for propulsion, whereas an electrically assisted vehicle, like an MHEV, uses its electric motor to assist a conventional internal combustion engine but not to fully power the vehicle on its own.
What are NEVs (Neighborhood Electric Vehicles)?
NEVs, or Neighborhood Electric Vehicles, are small electric vehicles designed primarily for low-speed driving (usually up to 25 to 35 miles per hour) in residential areas or city environments. They are ideal for short, daily trips and typically have a very limited range.
What is an Electric Road Vehicle?
Electric Road Vehicles refer to any electric vehicle designed for use on roads, including BEVs, PHEVs, HEVs, and MHEVs. They vary widely in performance, capacity, and the distance they can travel on a single charge or fuel tank.
Can electric vehicles be used for heavy-duty tasks like towing?
Yes, certain models of electric vehicles, especially some BEVs, are designed to handle heavy-duty tasks including towing. These vehicles are equipped with powerful motors and robust batteries capable of delivering the necessary torque and endurance needed for towing.

Imran is an experienced content writer who crafts engaging and informative articles for a variety of industries. With a keen eye for detail and a passion for storytelling, Imran delivers high-quality content that resonates with readers. Whether he’s writing blog posts, social media content, or website copy, Imran is committed to delivering compelling content that drives results.







